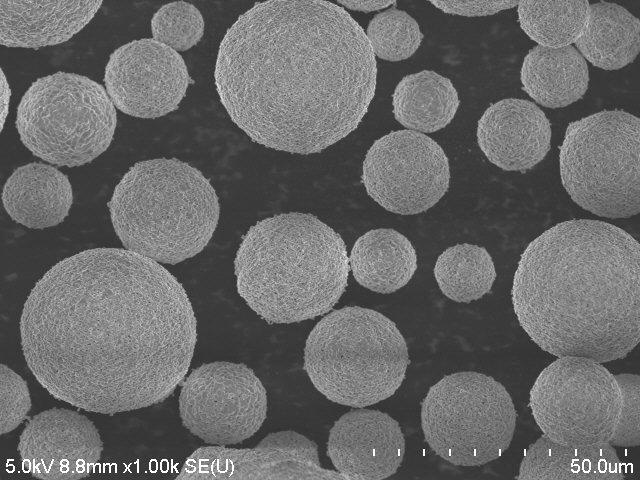
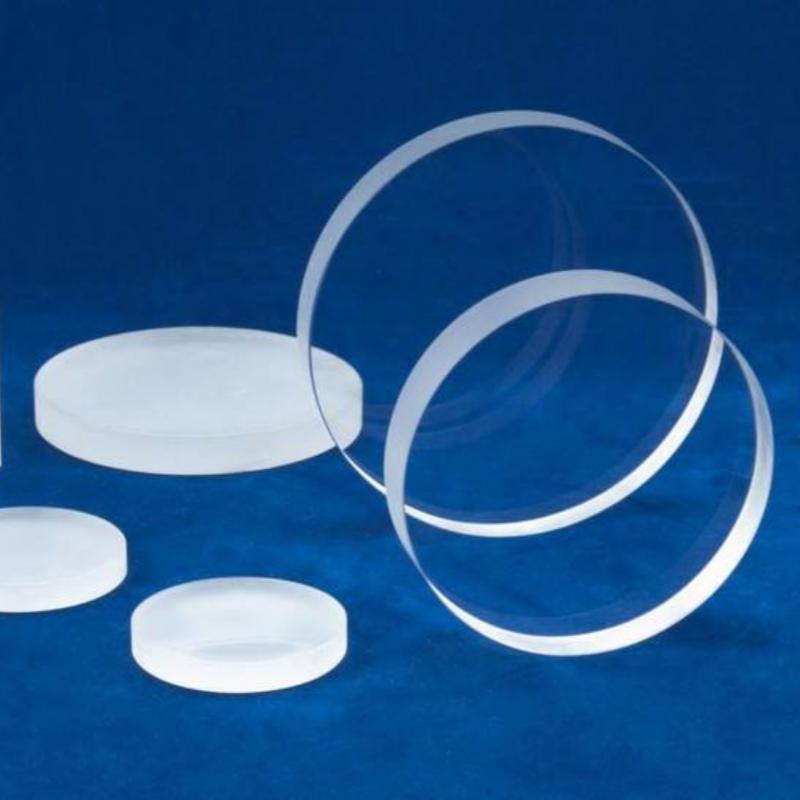
The application of rare earth in optical glass began at the end of the 19th century, mainly using CeO2 as a decolorizing agent for glass, in the late 1920s, Morey began to study borate glass of rare earth element oxides, and later countries carried out lanthanide borate optical glass research. In 1925, the United States Murray (G.N.Orey) began to study rare earth borate glass, and in 1938, the United States Kodak Company for the first time produced lanthanum containing optical glass with high refractive index and low dispersion characteristics, thus expanding the optical constant range of optical glass. Rare earth glass with more rare earth oxides introduced into the composition of optical glass has the characteristics of high refractive index and low dispersion. It is an indispensable optical material for manufacturing large aperture, wide field of view photographic objectives, long focal length, zoom lens and high-power microscope, etc. It is of great significance for improving the imaging quality and simplifying the design of optical instruments, especially camera objectives. Therefore, it has become a key material in the design of national defense military optical system.
At present, there are more than 300 kinds of optical glasses made of rare earth metal oxides in the world, which are widely used in aerospace, navigation, military, television and film, astronomy, geology and photography. There are many countries abroad that can produce rare earth optical glass, the main production countries are Japan, the United States, Germany, Russia, the United Kingdom, France and so on. In recent 20 years, China has made a lot of achievements in the study of rare earth optical glass, in silicate system, borate system, phosphate system, halide system and so on have made great progress. So far, China's production capacity of lanthanide optical glass has exceeded 2,500 tons/year, ranking first in the world, marking the advanced level of rare earth optical glass in China.